The emergence of enterprise-grade open source software (OSS) has fundamentally transformed the way in which organizations conceive, develop, and deliver products and services. This shift is equally applicable to the realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which has greatly benefitted from the widespread adoption of open source technologies and the formation of collaborative communities that foster cross-project integration.
In recognition of this trend, The Linux Foundation established the LF AI & Data Foundation in 2018 to facilitate a vendor-neutral environment where organizations, projects, and communities can collaborate and advance open source AI and data technologies. In addition, the Foundation has set out to provide guidance and support to developers, end-users, and leaders as they navigate the complex landscape of AI and data ecosystem.
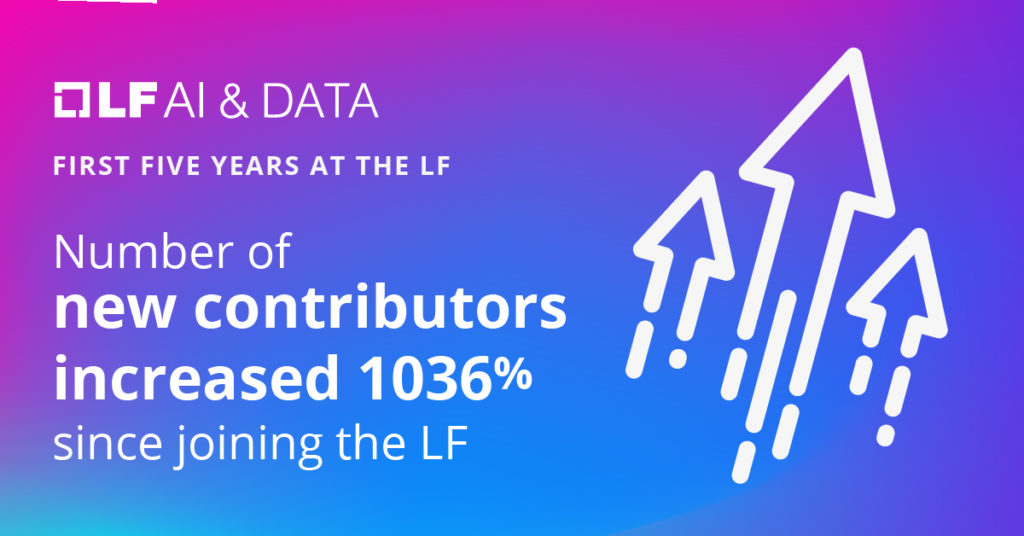
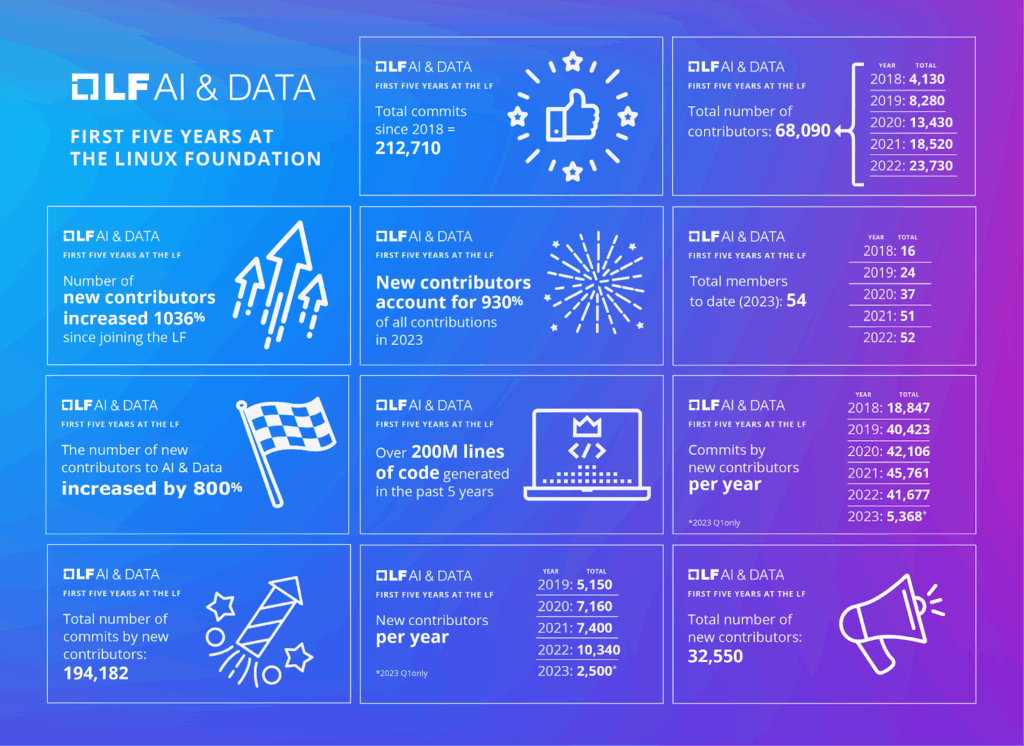
 Today, the Foundation hosts 47 active projects, and membership has grown to 55 member organizations. The efforts from these organizations have enabled cross-project collaboration while allowing additional participation and the formation of new projects. As a result, the community is increasingly engaged and more innovative together.
Today, the Foundation hosts 47 active projects, and membership has grown to 55 member organizations. The efforts from these organizations have enabled cross-project collaboration while allowing additional participation and the formation of new projects. As a result, the community is increasingly engaged and more innovative together.
- The LF AI & Data Foundation, in close collaboration with the wider community, has prioritized the pursuit of three key objectives that are integral to addressing the challenges faced by the industry. These include identifying the most effective strategies for promoting open source innovation in the domains of AI and data, cultivating a thriving and dynamic collaborative community, and consistently creating new opportunities for all members of the community. By focusing on these core goals, the Foundation and its members seek to drive innovation, foster collaboration, and create tangible value for all stakeholders in the AI and data landscape.
Notwithstanding the existence of a vibrant community, persistent challenges can impede the investment and adoption of open source projects. Frequently, organizations tend to steer clear of projects that face issues related to governance or integration limitations and instead opt to participate in and adopt more stable projects that adhere to an open and equitable governance model. As such, it is crucial for open source projects to prioritize the establishment of clear and transparent governance models to instill confidence among potential investors and users and foster a vibrant ecosystem that drives innovation and collaboration in the AI and data domains.
The LF AI & Data Foundation is taking decisive action to confront these ecosystem challenges by offering a neutral and inclusive hosting environment, designed to attract new contributors and support the growth of projects’ user bases and respective communities. Through this strategic approach, the Foundation aims to empower open source projects to achieve sustainable and scalable growth, enabling them to address the needs of the wider AI and data ecosystem while maintaining an open, transparent, and fair governance model.
Key trends in AI development
The AI and data ecosystem is a highly dynamic field that offers a multitude of opportunities for research, development, startups, and innovation. Several key trends are emerging that are likely to shape the future of AI. One such trend involves leveraging trusted and responsible AI, with a number of national and global initiatives underway to address concerns around fairness, explainability, and security in AI development. LF AI & Data and its member organizations view trusted and responsible AI as a critical domain and provide software toolkits to help achieve their goals.
Another key trend involves deriving insight and value from collected data, as digitalization and the transformation of industries and economies have led to abundant data. The challenge has now shifted from finding data to selecting and ensuring data quality, efficiently mining the data for actionable insights, and effectively converting those insights into business value.
Real-time decision-making is also driving advancements in AI toward the edge, unlocking a range of untapped possibilities for organizations. Edge AI allows thought leaders to address decreased latency, improved real-time analytics, and enhanced scalability in data processing, leading to improved performance.
Moreover, the recent surge in R&D in AI chip design is leading to a trend of infusing AI into hardware, where innovators aim to place AI directly on the silicon. Large organizations with deep pockets and startups with promising ideas see the AI chip as one of the most significant market opportunities in hardware today.
Finally, there is a growing demand for more efficient and intelligent algorithms, which presents a continuous opportunity for advancement. Both academia and industry are actively driving innovation in this field, introducing fresh concepts that pave the way for a new era characterized by smarter, faster, and highly efficient algorithms.
Collaborative efforts in AI development

* Companies hosting projects in LF AI & Data: (URL: https://landscape.lfai.foundation/hosting)
The AI & Data industry flourishes from the availability of enterprise-grade open source software (OSS) and thriving communities. With seamless collaboration and integration across multiple projects, LF AI & Data plays a vital role in advancing open source AI. Through its member companies and projects, the Foundation continues to illuminate its instrumental contribution to the AI and data landscape.
LF AI & Data Project Spotlights
 feathr and Feast are two high-performance enterprise-grade projects that provide tools and platforms for data scientists, researchers, and developers to solve complex real-world problems more efficiently. Both of these platforms aim to provide a consistent view of features between training and production environments, which is essential for building effective machine learning models. Contributed by LinkedIn, Feathr is focused on deployment and supports materializing and deploying features online in production. On the other hand,
feathr and Feast are two high-performance enterprise-grade projects that provide tools and platforms for data scientists, researchers, and developers to solve complex real-world problems more efficiently. Both of these platforms aim to provide a consistent view of features between training and production environments, which is essential for building effective machine learning models. Contributed by LinkedIn, Feathr is focused on deployment and supports materializing and deploying features online in production. On the other hand,
 A collaboration between Gojek and Google in 2018, Feast focuses on discovery and metadata tracking to promote feature reuse. By managing and streamlining the feature engineering process, these tools help reduce data duplication and improve consistency, accuracy, and reusability of data. This, in turn, can help accelerate model development and deployment, leading to more efficient and effective AI systems.
A collaboration between Gojek and Google in 2018, Feast focuses on discovery and metadata tracking to promote feature reuse. By managing and streamlining the feature engineering process, these tools help reduce data duplication and improve consistency, accuracy, and reusability of data. This, in turn, can help accelerate model development and deployment, leading to more efficient and effective AI systems.
 Horovod is a framework for distributed deep learning training created by Uber. It aims to simplify training deep learning models on multiple GPUs while improving performance and reducing training time.
Horovod is a framework for distributed deep learning training created by Uber. It aims to simplify training deep learning models on multiple GPUs while improving performance and reducing training time.
Horovod addresses these goals in two ways. First, it minimized the code change required to distribute a program. This means that data scientists, researchers, and AI developers can easily adapt their existing programs for distributed training without significantly changing their code. Secondly, Horovod makes it easy to run a program in a distributed way. The framework has high scaling efficiency for popular deep learning models such as Inception V3, TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, and Apache MXNet.
![]() Amundsen is a tool that helps data analysts, data scientists, and engineers work more efficiently by improving their ability to find and understand data. With Amundsen, users can easily search for data assets, see how data is connected, and assess data quality. This makes using data effectively in machine learning and AI applications faster and easier. Overall, Amundsen streamlines the data discovery process and enhances productivity for those working with data.
Amundsen is a tool that helps data analysts, data scientists, and engineers work more efficiently by improving their ability to find and understand data. With Amundsen, users can easily search for data assets, see how data is connected, and assess data quality. This makes using data effectively in machine learning and AI applications faster and easier. Overall, Amundsen streamlines the data discovery process and enhances productivity for those working with data.
 Milvus is a database that was created in 2019. It was designed to store, manage, and index large embedding vectors that are created by deep neural networks and other machine learning models. This is important in many applications related to AI and data because it provides a fast and flexible solution for managing large amounts of vector data. Because Milvus is open source and compatible with machine learning frameworks, it is a valuable tool in the Ai and data community.
Milvus is a database that was created in 2019. It was designed to store, manage, and index large embedding vectors that are created by deep neural networks and other machine learning models. This is important in many applications related to AI and data because it provides a fast and flexible solution for managing large amounts of vector data. Because Milvus is open source and compatible with machine learning frameworks, it is a valuable tool in the Ai and data community.
 OpenFL is a Python 3 library for federated learning, a decentralized approach to machine learning. It allows organizations to train or validate models collaboratively without sharing sensitive information. Instead of moving private data to a central location, the model is sent to the data for training or validation.
OpenFL is a Python 3 library for federated learning, a decentralized approach to machine learning. It allows organizations to train or validate models collaboratively without sharing sensitive information. Instead of moving private data to a central location, the model is sent to the data for training or validation.
OpenFL can work with frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch. The project aims to develop a flexible, secure, and scalable federated learning library accessible to data scientists. It enables decentralized training and validation of AI models while preserving privacy and security.
This project has recently taken the GAAD Pledge to improve accessibility for developers. By making accessibility a core value, the project enables developers of all abilities to contribute effectively, creates an inclusive environment, and revolutionizes how we build AI.
 Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART) is a Python library that provides tools to evaluate, defend, certify, and verify machine learning models and applications against adversarial attacks.
Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART) is a Python library that provides tools to evaluate, defend, certify, and verify machine learning models and applications against adversarial attacks.
ART supports many machine learning models, including deep neural networks, support vector machines, logistic regression, and more. It also provides several defense mechanisms to improve the robustness of machine learning models against adversarial attacks, such as adversarial training, gradient regularization, and input sanitization.
ART’s contributions to AI and data development are significant. Adversarial attacks are a significant threat to the security and reliability of machine learning models, and ART helps address this issue by providing tools for robustness and security. It also promotes transparency and trust in machine learning models by enabling researchers and developers to evaluate and verify their models’ robustness against adversarial attacks.
Conclusion
Industry-leading companies contribute to these projects; by making the source code publicly available, and through the nature and spirit of the open source ecosystem, they contribute to the AI and data landscape by making these capabilities more accessible to a broader range of organizations and individuals.
“We are in a unique position to drive open innovation in AI & Data with our collaborative approach that supports a neutral environment, open governance, and engaged and dedicated communities,” said Dr. Ibrahim Haddad, Executive Director of LF AI & Data Foundation. “We have witnessed incredible advancements in the field of AI & Data by embracing open source technologies with a transparent governance model. By working together, we accelerate the pace of innovation and push the boundaries of what is possible in the AI and data landscape.”
We look forward to what the next five years brings to the AI & Data and open source community. Come join us!