In the ever-evolving landscape of conversational AI, interoperability is pivotal to creating seamless and intuitive user experiences. On September 17, a session of our TAC Talks series, hosted by Vini Jaiswal, Chair of the Technical Advisory Board at the LF AI & Data, featured insights from Deborah Dahl, Principal of Conversational Technologies.
To watch all previous TAC Talks, please visit the YouTube playlist.
Key Features and Technical Specifications
The session delved into the technical framework underpinning the initiative, outlining three primary types of messages that facilitate inter-assistant communication:
- Assistant Manifest: This message allows an assistant to describe its own capabilities, akin to how a website presents its content. It includes parameters like service endpoints, capabilities, key phrases for discovery, and supported languages. For example, an immigration specialist chatbot would use its manifest to indicate expertise in visa-related queries.
- Conversation Envelope: Serving as the communication bridge, this message contains metadata such as speaker identity, timestamp, and the actual user utterance. It ensures that messages are transmitted accurately and contextually between assistants.
- Dialogue Events: These represent the natural language interactions between users and systems, enriched with metadata and potentially additional information like audio or custom features developed by chatbot developers.
The initiative emphasizes simplicity and flexibility, allowing for easy implementation. As Deborah highlighted, “All that has to be done to become interoperable is to be able to send and receive messages like this.” This minimalistic approach ensures that even organizations with limited technical resources can adopt the standards effectively.
Practical Use Cases: From Government to Smart Homes
The session also showcased several compelling use cases demonstrating the initiative’s real-world applicability:
- Government Applications: Estonia’s government serves as a prime example. Faced with managing numerous administrative chatbots across various departments, Estonia adopted the Open Voice Interoperability specifications to create a cohesive system. This allows citizens to interact with a unified interface that seamlessly redirects queries to the appropriate department, enhancing efficiency and user satisfaction.
- Large Organizations: Within vast institutions like universities or multinational corporations, different departments often maintain their own chatbots. This leads to inconsistent user experiences and increased complexity for users navigating between services. The initiative’s standards facilitate interoperability, ensuring that users receive a unified and streamlined interaction regardless of the department or service they engage with.
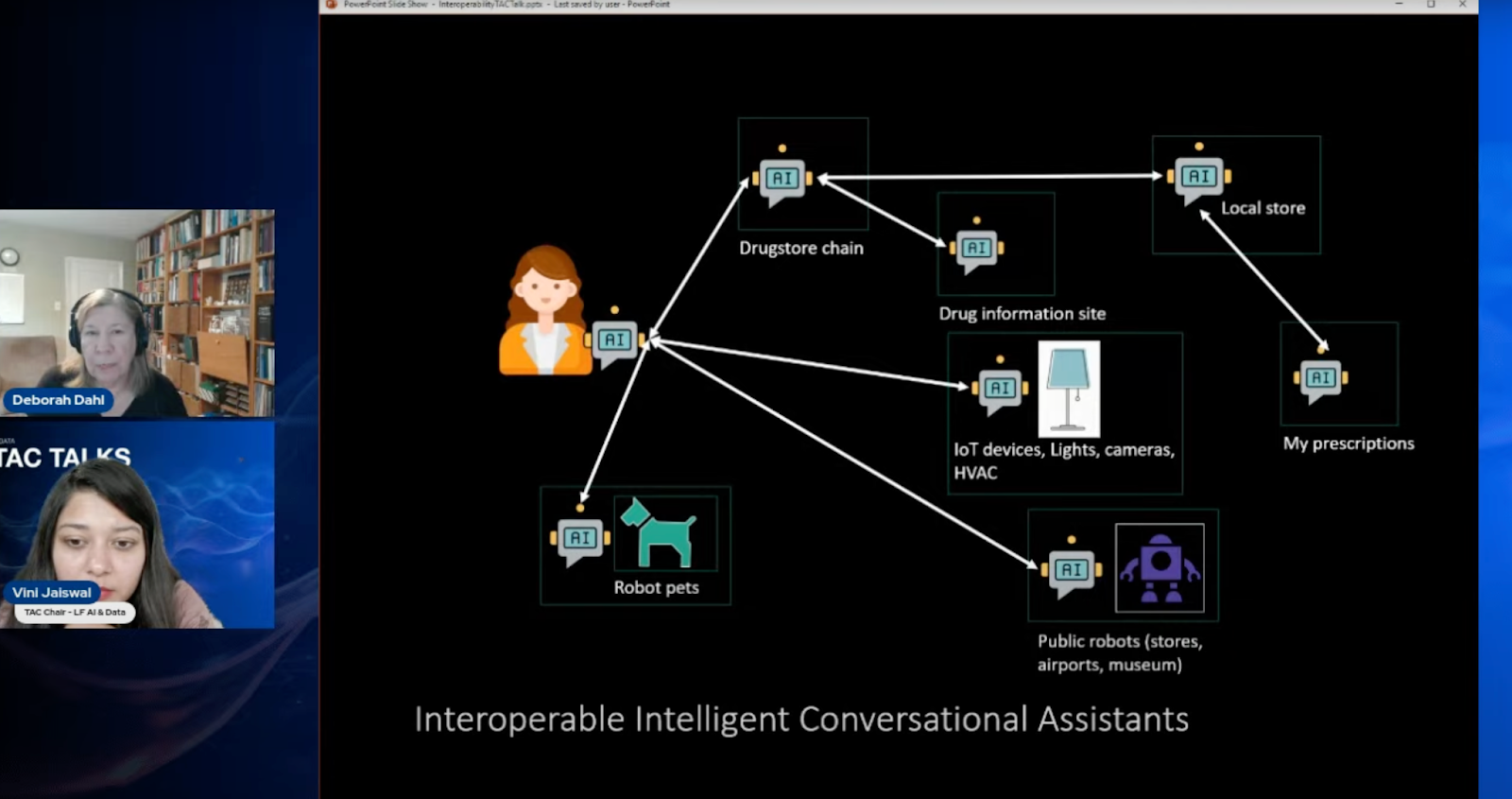
- Consumer Personal Assistants: Imagine interacting with a personal assistant that effortlessly manages interactions across multiple vendors—be it your grocery store, pharmacy, or local service providers. By adopting the Open Voice Interoperability standards, personal assistants can provide a cohesive experience, saving users time and reducing the friction of switching between different service interfaces.
- Smart Homes and IoT Devices: The initiative also envisions a future where IoT devices communicate seamlessly. For instance, integrating in-home smart devices allows users to manage their smart home environment through a single, unified conversational interface.
Sandbox Implementation and Open Source Collaboration
To demonstrate the practicality of their specifications, the Open Voice Interoperability Project has developed a Sandbox Implementation, a web-based system that supports both text and speech interactions. Hosted on GitHub, the sandbox includes sample assistants like “The Wizard,” a general-purpose AI agent, and “Athena,” a specialized assistant focused on books and authors. These samples illustrate how different assistants can be integrated and interact within the standardized framework.
Developers and enthusiasts are encouraged to explore the Open Voice Interoperability GitHub Repository for comprehensive documentation, implementation guides, and additional resources. The repository provides step-by-step instructions for setting up the sandbox, building custom assistants, and contributing to the evolving standards.
Future Roadmap and Community Engagement
The discussion concluded with a glimpse into the future roadmap of the initiative. Deborah outlined plans to enhance chatbot interactions further, enabling not just sequential conversations but also multi-assistant dialogues. For example:
- Hospital Use Cases: In a hospital setting, different specialized chatbots (e.g., for admissions, surgery scheduling, patient records) could collaborate to determine the optimal placement for a patient, ensuring all necessary factors are considered efficiently.
- Trip Planning: Travel planning could become more intuitive, with flight assistants, hotel booking bots, and local event coordinators working in tandem to provide comprehensive and personalized trip recommendations without redundant steps.
Building the Future of Conversational AI Together
The Open Voice Interoperability Initiative represents a significant leap towards creating a more connected and user-friendly conversational AI ecosystem. By establishing open standards and fostering collaboration, the initiative aims to eliminate the fragmentation that currently hampers user experiences across various platforms and services.
“With this little bit of interoperability and very simple specifications, the possibilities are endless,” said Vini Jaiswal. The session concluded with an invitation for developers, organizations, and enthusiasts to join the movement, contribute to the open-source efforts, and participate in upcoming events to shape the future of conversational AI.
For those interested in getting involved, follow the Open Voice Interoperability Project on LinkedIn and X and visit the GitHub repository.
Stay tuned for more insightful sessions in our TAC Talks series, happening biweekly on Tuesdays at 9 a.m. Pacific Time.
LF AI & Data Resources
- Learn about membership opportunities
- Explore the interactive landscape
- Check out our technical projects
- Join us at upcoming events
- Read the latest announcements on the blog
- Subscribe to the mailing lists
- Follow us on Twitter or LinkedIn
Access other resources on LF AI & Data’s GitHub or Wiki